- Accident definition in safety (occupational health and safety)
- Causes of workshop accidents
- Safety definition in the industry
- General safety precautions
- examples of personal safety risks
- proper use of hand tools and equipment
- Safety with the machine
- Safety in Workshop
- FIRE DEFINITION AND MEANING
- Safety with Drilling Machines
- Safety with Grinding
- Safety with Lathes
- Safety with Lifting Loads.
- What is the wooden top used on a workbench?
- How will you protect the sharp point of a scriber from causing injury when it is not in use?
- What special precaution will you take while parting off a job with a hand hacksaw?
- An operator was working on a bandsaw, which was not adequately protected. His left hand came in contact with the bandsaw and his two fingers were severed. How could have such an accident been prevented?
- A craftsman was hammering a mild steel bar on an anvil and a steel splinter from the hammer flew into his eye. The eye was lost. How could have such an accident been prevented?
An indispensable aspect of any profession revolves around Occupational Health and Safety (OHS), encompassing the meticulous safeguarding of employees’ well-being during their work tenure. This entails providing a secure working environment, free from perils and hazards, while simultaneously addressing the physical, psychological, and emotional aspects of employee health. Employers are mandated to adopt comprehensive measures to avert workplace mishaps and injuries, involving the meticulous assessment of risks, imparting appropriate training, furnishing state-of-the-art equipment, and fortifying work procedures. The domain of OHS further encompasses the establishment of foolproof contingency plans and ensuring the availability of proficient first-aid facilities. Moreover, it is of paramount importance to cultivate a work ambiance that fosters overall well-being by mitigating stress and promoting holistic tranquility.
Accident definition in safety (occupational health and safety)
An accident is an unplanned and non-controlled event in which the action or reaction of an object, substance, or person results in personal injury or probability thereof.
Results of Accidents:
Accidents result in the following —
- Complete loss of factory and equipment.
- Partial loss of equipment or building.
- Loss of production.
- Loss of lives of employees. Permanent disablement for the persons.
- Loss of limbs, eyesight, hearing, etc.
- Disablement for the day or for a short period.
Causes of workshop accidents
Human Causes:
Carelessness and overconfidence cause accidents
Hand Tools:
Suitable tools must always be selected for the given particular work. Accidents may occur if faulty or improper tools are used.
Working Conditions:
Slippery floors, poor ventilation, poor lighting, and inadequate space are potential causes of accidents.
Machines:
Unguarded machinery, poor maintenance, improper adjustments, etc. can cause accidents.
Materials:
Storage of inflammable materials in unsecured places can lead to grave accidents. Sharp and pointed tools and jobs can also cause accidents.
Person himself:
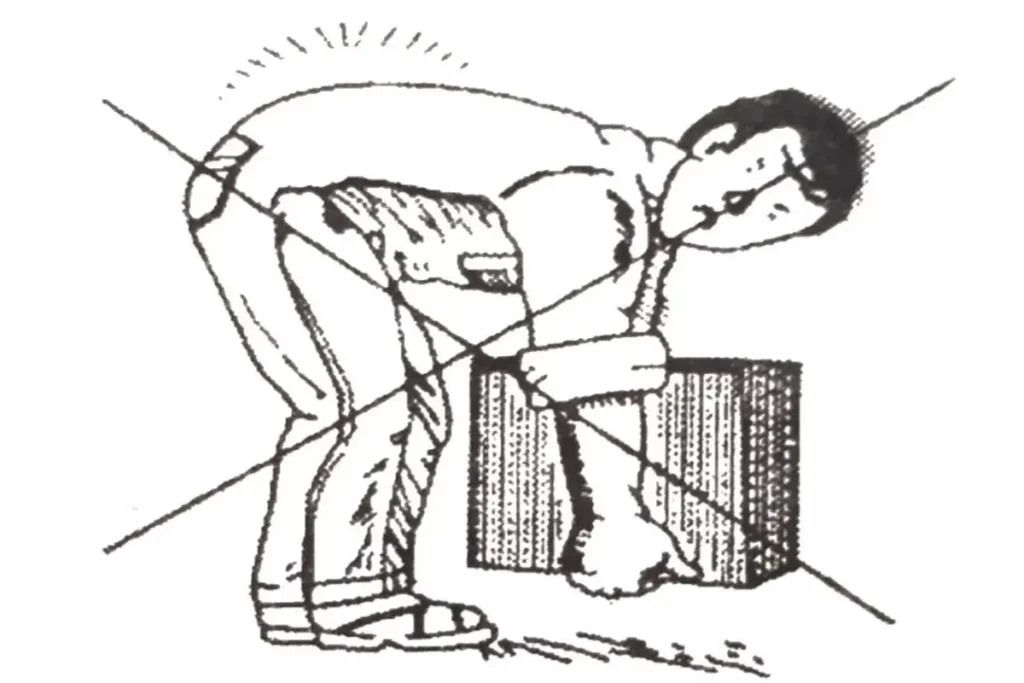
An improper and/or uncomfortable dress as well as an improper position or posture can cause an accident at the workplace.
Safety definition in the industry
A good craftsman is one who is safety conscious. He knows and puts into practice safe and accepted procedures. Learning to work safely is as important as learning the trade itself. Safety is an action that organizes and controls all our acts in such a manner that we don’t get involved, or expose ourselves or others in an accident. Many accidents happen because people don’t behave sensibly in the workshop.
General safety precautions
- Learn the safe way of doing the job before you actually start.
- Think of safety and act safely at all times.
- Follow all the safety rules and regulations-they are meant to protect you.
- Put on proper and protective clothing.
- Don’t indulge in horseplay.
- Concentrate on the work and avoid unnecessary talking.
- Handle only the equipment you have been authorized to work on.
- Check up and inspect the tools for safe working from time to time.
- Don’t attempt to oil, clean, adjust or repair any machine when it is running.
- Don’t try to stop a machine with your hands or body.
examples of personal safety risks
- Keep your feet, hands, and clothing away from moving engine and equipment components.
- Use eye protection when you work with engines or power tools.
- Wear ear protection to reduce the risk of gradual hearing loss from exposure to engine noise.
- Wear a face mask, if required, when working with chemicals.
- Wear specially designed gloves to protect against heat, harmful chemicals, and sharp objects.
- Wear safety shoes to protect against falling objects. Safety shoes have soles that won’t deteriorate when exposed to gasoline or oil.
proper use of hand tools and equipment
- Avoid split, broken, and loose handles of hammers. Heads of hammers must not be worn and they must be securely fastened to the handle.
- Files must never be used as levers. They should always have a proper handle fitted to them.
- Chisels with mushroom heads are dangerous. When chipping always make sure that chips do not heat somebody standing nearby.
- Always hold the work firmly in a vice or other holding device. If the work shifts during operation a nasty injury may result.
- Always use the correct size of the spanner and avoid the use of packing or extension handles.
- Always use a screwdriver that fits correctly in the screw head. Do not hold the work in hand while tightening or loosening a screw. The screwdriver may slip and cause injury to the hand.
Safety with the machine
- Do not try to operate any machine before you fully understand its mechanism.
- Be sure how to stop a machine before you start it.
- Never operate a machine unless all safety guards are in position.
- Always keep the shop floor free from oil, grease, tools, and other cuttings.
- Job must be adequately clamped.
- The cutter must be held properly. Only recommended speeds and feeds should be used.
- Use a cleaning brush to clear off the swarf from the machine.
- Do not attempt to measure the job when it is in a moving position.
- Do not try to change gears when the machine is in the running position.
- Do not try to stop the rotating tool/job by hand.
- Only recommended lubricants and coolants should be used.
- The grinding wheel should be checked for cracks before fitting it.
- Switch off power while mounting or dismounting a chuck and removing the job from the machine. The Chuck key must be removed before starting the machine.
- A wooden plank should be used on bed ways of the lathe while mounting and dismounting the chuck.
- Get first aid immediately for any injury.
Safety in Workshop
- Keep the shop floor clean and free from grease, oil, or other slippery material.
- Clean the floor frequently.
- Keep passages, gangways, and pathways clear to avoid accidents.
- Keep all the materials in their proper places. Put all unnecessary and rejected items and scrap in a scrap box.
- Store tools in their places when not in use.
- Provide proper light, ventilation, etc.
FIRE DEFINITION AND MEANING
Safety with Drilling Machines
- Remove the chuck wrench from the drill chucks, before starting the machine.
- Check frequently whether the drill is running true or not.
- Use only sharpened drills of the correct size.
- Ensure that proper speeds and feeds are used.
- All the burrs from drilling holes should be removed by scraping or filing.
- Change the belt or speed only after the power is put off.
- If the work slips from a clamp, don’t attempt to stop it, but stop the machine and then make the necessary adjustment


Safety with Grinding
- Always use goggles or face shields while working on a grinder.
- Check the various parts and controls before the grinder is set in motion.
- Ensure that the wheel is flat and free from depressions and grooves.
- Use only correct and sound wheels for the work.
- Ensure that the tool rest in the pedestal grinders is about 3 mm from the face of the wheel. If the clearance is more it may cause the job to jam the wheel and break it.
- Use the entire face of the wheel and not any particular portion to ensure uniform wear of the wheel.
- Use only the face of the wheel and not the side of the wheel unless specified.
- The wheel should be run at a specified speed only.
- Check frequently the balance of the wheel.
- Use proper holding devices or clamps while grinding small pieces.
- Check the holding power of the chuck before starting the machine in the case of surface grinders.
Safety with Lathes
- Check salient points before switching on the power supply.
- Ensure that the tailstock, tool holder, and job are properly clamped.
- Use wooden planks over the bed while putting or removing the chuck or face plate or another part.
- Do not leave the chuck key on lathe chucks, as the key may fly during starting.
- Don’t keep anything on the lathe bed.
- Don’t use a wrench on revolving parts.
- Don’t measure work or feel the edge or check the job or adjust the cutting tool while the lathe is running. Don’t try to take heavy cuts on thin work.
- Don’t shift or change gears while the lathe is running.
Safety with Lifting Loads.
- Before lifting loads, make sure the route is clear of obstacles.
- The place where the load is to be placed should not be obstructed.
- The person who is carrying the load should be able to see over and around it.
- The load should be lifted according to age, physique, and health condition.
- Do not lift a load that may cause strain in your body because twisting or jerking during lifting can put severe strain on muscles
Lift the load properly. Approach the load squarely facing the direction of travel [Fig. 1.6(a)]. First, straighten the legs to raise the load [Fig. 1.6(b)]. Look directly ahead while straightening up and keep the back straight [Fig. 1.6(c)]. Keep the load well into the body and carry it to the place where it is to be placed [Fig. 1.6(d)].
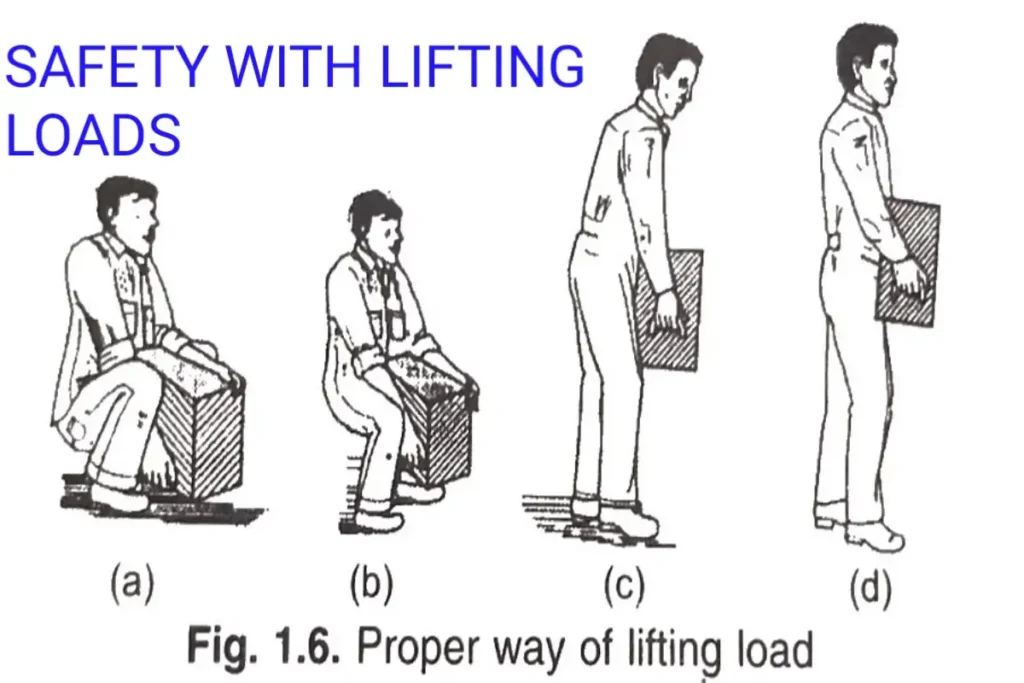
For lowering the load, bend at the knees to a semi-squatting position and keep the back and head erect by looking straight ahead. Lower the load and place it at the required place.
What is the wooden top used on a workbench ?
Because wood can absorb shocks and also does not damage the finished component.
How will you protect the sharp point of a scriber from causing injury when it is not in use ?
By covering the sharp point with card board/cork piece.
What special precaution will you take while parting off a job with a hand hacksaw ?
Reduce the pressure just before the pieces separate.
An operator was working on a bandsaw, which was not adequately protected. His left hand came in contact with the bandsaw and his two fingers were severed. How could have such an accident been prevented ?
Prevision of guard on the blade and safe working method would have prevented the accident.
A craftsman was hammering a mild steel bar on an anvil and a steel splinter from the hammer flew into his eye. The eye was lost. How could have such an accident been prevented ?
Better maintenance of hammer and use of safety goggles would have prevented the accident.